Install
1) For Window (win64 version of MolAICal):
Firstly, decompress the downloaded MolAICal file. Secondly, if MolAICal is placed on E: disk, change into the directory path of MolAICal in DOS or Powershell by below commands (Users should modify them according to the actual path of MolAICal):
#> e:
#> cd E:\test\log\MolAICal-win64
At last, input the below command and press Enter Key for installation:
#> install.bat
It should be like the below terminal:
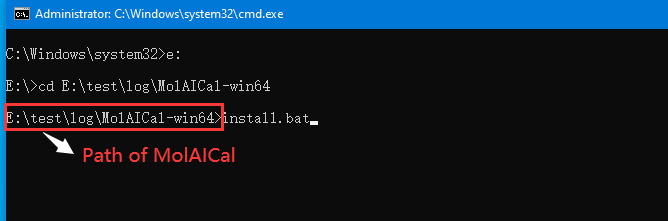
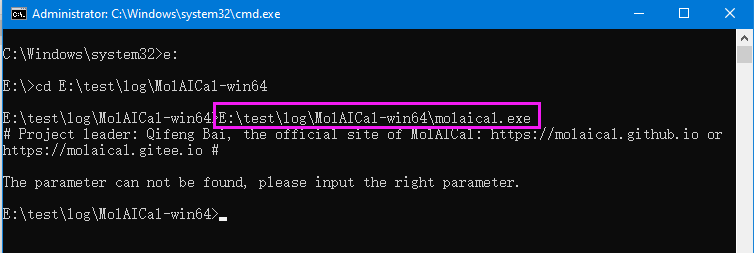
MolAICal is a command-line tool. Users can use the absolute path of MolAICal on DOS or Powershell of Windows. To test MolAICal running, for example: if MolAICal is placed on the E: disk, then users can run the blow example command (Users should modify it according to the actual path of molaical.exe):
#> E:\test\log\MolAICal-win64\molaical.exe
Press Enter Key, it should show similar message as follows:
Until now, install and test are complete.
2) For Linux (linux64 version of MolAICal):
Install steps are in Linux terminal console as follows:
1) tar -xzvf MolAICal-linux64-xxx.tar.gz
Notice: Please replace the corrected characters in MolAICal-linux64-xxx.tar.gz according to your downloaded MolAICal.
2) cd MolAICal-linux64-xxx
3) chmod +x install.sh
4) ./install.sh
Note: installing MolAICal on a Linux system requires starting (or removing and starting) a container and image, which is relatively time-consuming—please be patient. If the user wishes to install MolAICal in the background or has a limited terminal session time, they can use the command:
./install.sh >& log &
to perform a background installation.
At last, users can run the blow example command in Linux terminal console (Users should modify it according to the actual path of molaical.exe):
#> /home/fly/bai/MolAICal-linux64/molaical.exe
Press Enter Key, it should show similar message as follows:
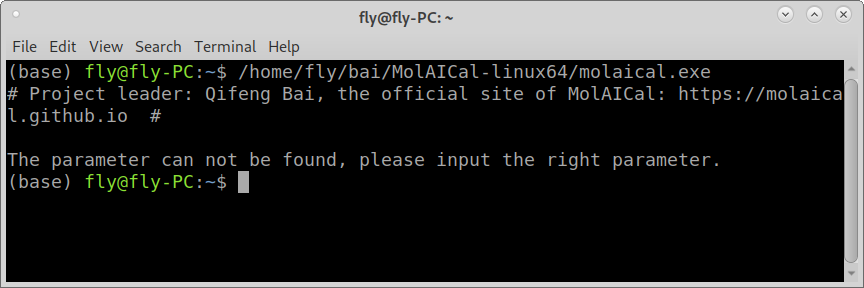
Until now, installation and testing are complete.
1) To use MolAICal expediently, users can set system path of MolAICal. So the command molaical.exe can be used without given path.
Notice: MolAICal only provides Windows and Linux 64-bit versions. Users should not change the name or path of MolAICal after install is complete in Linux System. If users change the name or path of MolAICal, please re-install MolAICal again.
2) Since the Linux version of MolAICal launches a persistent container that runs continuously, users can remove, uninstall or stop this container of MolAICal using the following commands:
#> molaical.exe -eset sys rm molaical
#> molaical.exe -eset sys rmi molaical:v9
3) Possible install issues (option):
If MolAICal images and containers have already been loaded previously, MolAICal will first remove these images and containers. If similar errors occur as below:
rm: cannot remove '630b0b26-296e-3f17-a1b7-e4effdf77bba/ROOT/usr/bin': Directory not empty
the following command can be executed to forcefully remove the container:
1) Enter P1 mode:
usage: molaical.exe -eset sys setup --execmode=P1 containerIDNAME
e.g.,
#> molaical.exe -eset sys setup --execmode=P1 molaical
or
#> molaical.exe -eset sys setup --execmode=P1 30754628-67fe-3109-bfd3-00a830163ee5
And then:
#> cd ~/.udocker/containers/
#> rm -rf <container folder>
4) Linux Version of MolAICal: Architecture and Acceleration
As shown in the below Figure, the MolAICal container can not only utilize the container system's files and programs but also access the host machine's library files through mounting and mapping mechanisms. This effectively resolves issues such as library conflicts or missing dependencies. However, program execution within containers may indeed be slower than on the local machine.
The below Figure demonstrates that due to the mapping relationship, the computational commands executed by "molalcal.exe" in the container are identical to those run by "molaical.exe" on the local machine.
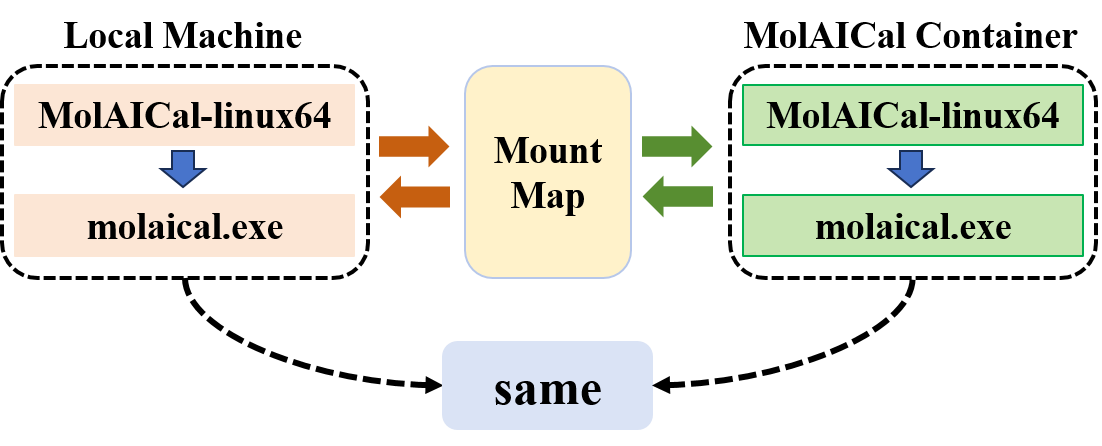
Architecture Diagram for the Linux Version of MolAICal
Therefore, to improve the running speed, for tasks with minimal library dependencies—such as virtual screening using MolAICal—consider copying MolAICal from the container to the local machine:
a). Go to the container file system, it will enter the "/root"
#> molaical.exe -eset shell in
b). The first part of 'cp' is from the MolAICal container, and the second part is in the local machine
#> cp -r soft/MolAICal-linux64 <local machine directory>/
c). Exit container file system
#> exit
At last, performing virtual screening locally via the same methodology can significantly accelerate the screening process.
5) Useful website Links:
MolAICal is designed based on OpenJDK. We collect the websites for downloading OpenJDK:
1. https://openjdk.java.net/
2. https://adoptopenjdk.net/
3. https://www.azul.com/downloads/zulu-community/
4. https://github.com/ojdkbuild/ojdkbuild
5. https://github.com/openjdk/jdk